Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Data Farm
Inc.ฎ
|
The Technical "Know-How"
|
Web Services Tier - Why Make It Harder
Web services provide a cost-effective way of distributing corporate data. We have a new
way of thinking in how to build web services for
web, mobile and/or any new technologies. To present our approach we are going to cover
some basic concepts of existing web services, our view such these existing web services
and then we would present our new approach. The Web Services Tier image is our proposed
Web Services Tier for our Post Office project.
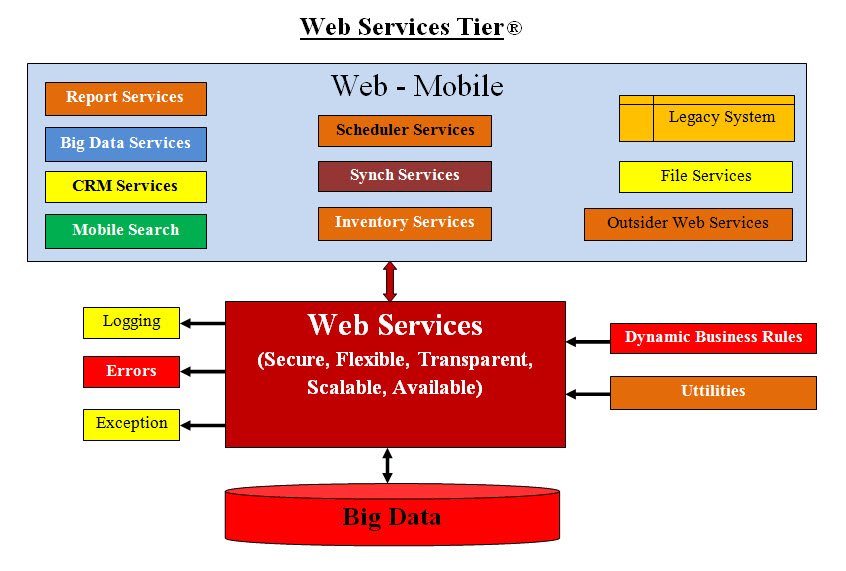
Types of Web Services:
In a nutshell, web services can be:
Database dump of one company (possibly a Legacy System) to another
File Services (FTP site or any remote data services)
Outside Web Services
Scheduler-Synch-Inventory Services
Big Data or CRM vendors data updates
Mobile requests for simple search which would return one line of text
Report Services (such as statistics)
Web services should be secure, flexible, transparent, available and automated to
meet the clients requests without constant recoding and revising the running web services.
It should also have its own dynamic Business Rules. The incoming and outgoing data should be connected a database.
The W3C defines a Web service generally as:
A software system designed to support interoperable machine-to-machine interaction over a network.
Web services are open standard (XML, SOAP, HTTP etc.) based Web applications that interact with
other web applications for the purpose of exchanging data. The basic standards for web services are:
XML (Extensible Markup Language)
SOAP (simple object access protocol)
WSDL (web services description language)
UDDI (universal description, discovery and integration)
HTTP, SMTP are still used over TCP/IP to pass the messages.
All Web Services documents are written in XML
XML Schema are used to define the elements used in Web Services communication
How Does a Web Service Work?
A web service enables communication among various applications by using open standards
such as HTML, XML, WSDL, and SOAP. A web service takes the help of:
XML to tag the data
SOAP to transfer a message
WSDL to describe the availability of service.
SOAP:
Communicate with the Web Service
Both the request and the response are SOAP messages
The body of the message (whose grammar is defined by the WSDL) is contained within a SOAP envelope
Binds the client to the web service
Security and Web Services:
Web services security requirements are supported by industry standards both at the transport
level (Secure Socket Layer) and at the application level relying on XML (XML Encryption and XML digital signature).
Web Services for Mobile:
To integrate Web Service technologies in mobile devices one has to consider the restrictions of
these devices and the mobile communication system. Mobile devices have several limitations, such
as slow Central Processing Units (CPUs), memories, primitive operating systems and small
displays. Mobile communication systems, especially GPRS and UMTS, imply limited bandwidth and high latencies.
RESTful Web Services:
In Java EE 6, JAX-RS provides the functionality for Representational State Transfer (RESTful) web
services. REST is well suited for basic, ad hoc integration scenarios. RESTful web services, often
better integrated with HTTP than SOAP-based services. RESTful web services do not require XML
messages or WSDL serviceAPI definitions.
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON):
JSON is syntax for storing and exchanging text information. Much like XML, JSON is smaller
than XML, and faster and easier to parse. JSON is lightweight text-data interchange format. JSON
is language independent. JSON uses JavaScript syntax for describing data objects, but JSON is
still language and platform independent. JSON parsers and JSON libraries exists for many different
programming languages. JSON is "self-describing" and easy to understand.
Our view:
In a nutshell, web server is nothing more than communicating using XML. XML is also nothing but
structured text files which we have tools that build them and other that read/parse them. There
are a number of tools such as Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS) and Java API for RESTful
Web Services (JAX-RS). There are number of companies built their own homegrown web services with their schemas.
Our Approach:
We look at the data for web services as both:
Incoming
Outgoing
Incoming Data:
The Incoming data can be any format (XML, PDF, spreadsheets, text, forms, ... etc) where we
would be building parses to convert such data into our DAO-XML files that would be store in our database as XML field.
Outgoing Data:
Our Outgoing data would be converted to any format our clients would request. We also provide
DAO-XML files, Interactive plug-ins, templates or even web pages.
Security:
Check Security and Compression-Encryption pages in this site.
|
|